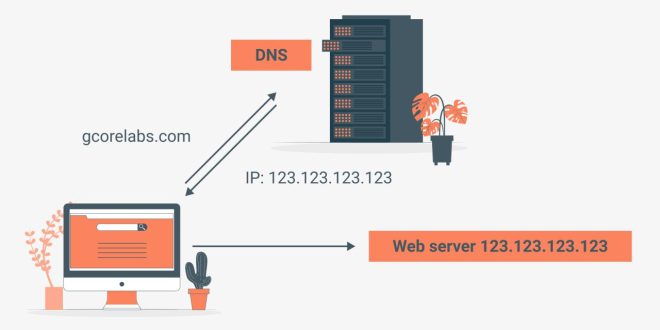
In today’s digital landscape, every website, email, and online service relies on a crucial yet often overlooked service known as DNS hosting. Without DNS, the internet as we know it would cease to function, as it’s the invisible force that translates human-readable domain names like ‘google.com’ into the numerical IP addresses that computers understand.
DNS hosting ensures that our online interactions are seamless, allowing us to access websites, send emails, and engage with the digital world effortlessly. However, managing DNS records can be a complex task, often requiring technical expertise and constant maintenance.
This article will delve into the intricacies of DNS hosting, shedding light on the challenges and best practices involved in keeping your online presence accessible and secure.
DNS Hosting: The Ultimate Guide
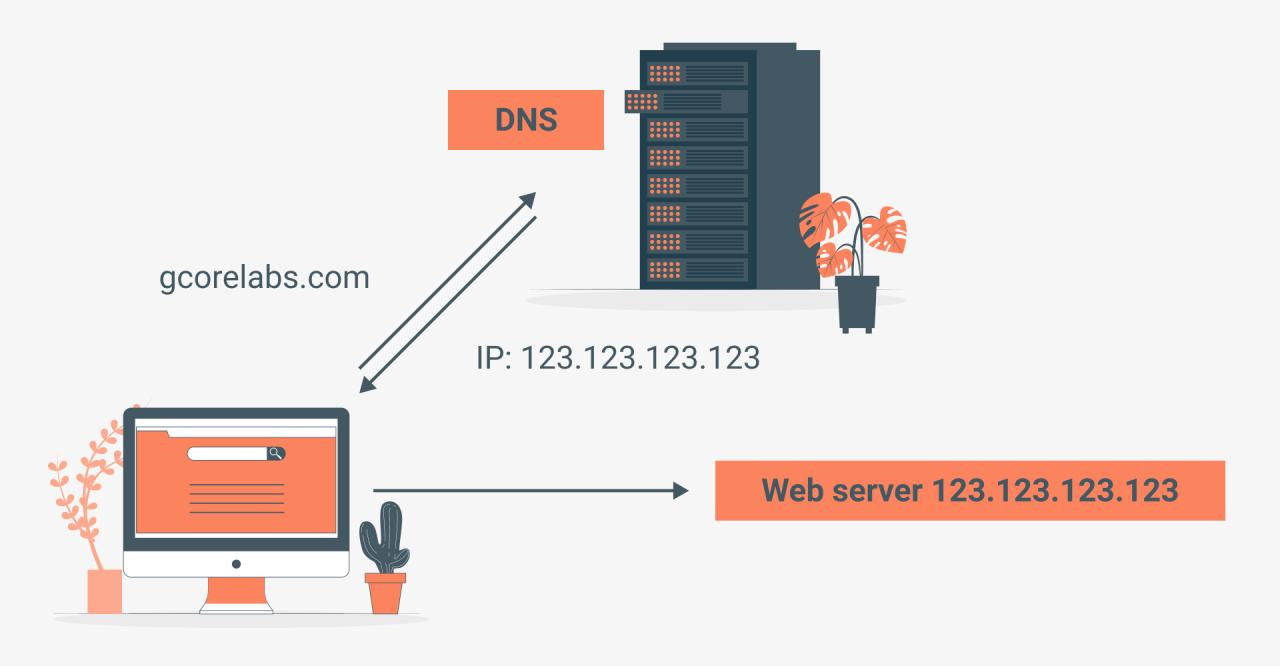
In the realm of the internet, DNS hosting plays a crucial role in bridging the gap between human-readable domain names and the numerical IP addresses used by computers to locate websites and other online resources. This behind-the-scenes service acts as a directory, translating domain names like “example.com” into their corresponding IP addresses, ensuring that users can seamlessly access websites without memorizing complex numerical addresses.
Why DNS Hosting Matters
DNS hosting is vital for several reasons:
• Improved user experience: Users can access websites using easy-to-remember domain names instead of intricate IP addresses, enhancing their online experience.
• Website accessibility: DNS hosting ensures that websites are readily available by translating domain names into IP addresses, allowing users to connect to websites swiftly and reliably.
• Website performance: Efficient DNS hosting can improve website performance by minimizing the time it takes to resolve domain names, resulting in faster page loading speeds.
How DNS Hosting Works
DNS hosting operates through a decentralized network of DNS servers, each containing a portion of the DNS database. When a user enters a domain name into their browser, a series of queries are initiated to locate the corresponding IP address.
The DNS servers work together to resolve the domain name, returning the IP address to the user’s browser, which then establishes a connection to the website.
Types of DNS Hosting
DNS hosting services come in various types to suit different needs:
• Free DNS hosting: Provides basic DNS hosting services at no cost, suitable for personal websites or small businesses with limited requirements.
• Paid DNS hosting: Offers more advanced features, such as enhanced security, faster performance, and dedicated support, ideal for businesses and organizations.
• Cloud DNS hosting: Leverages the scalability and reliability of cloud computing, providing flexible and cost-effective DNS hosting solutions.
Choosing the Right DNS Hosting Provider
Selecting the right DNS hosting provider is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and reliability. Consider the following factors:
• Reliability: Choose a provider with a proven track record of uptime and stability to minimize website downtime and ensure consistent accessibility.
• Performance: Look for providers with fast DNS resolution times and the capacity to handle high traffic volumes without compromising performance.
• Security: Opt for providers that offer robust security measures to protect against DNS attacks, such as DDoS protection and DNSSEC.
• Features: Evaluate the additional features offered by providers, such as traffic analytics, load balancing, and custom DNS records to meet your specific requirements.
• Support: Choose a provider with responsive and knowledgeable support to assist you with any technical issues or questions.
Conclusion
DNS hosting is an indispensable service that enables users to access websites seamlessly and efficiently. By understanding the basics of DNS hosting, its importance, and how to choose the right provider, you can ensure that your website is always accessible and performant for your users.
Advanced DNS Record Types
Beyond the basic DNS records like A, CNAME, and MX, there are several advanced record types that serve specific purposes:
• TXT records: Store arbitrary text data associated with a domain name, often used for verification purposes or to provide additional information.
• SRV records: Specify the location of specific services on a domain, such as the mail server or the instant messaging server.
• AAAA records: Provide the IPv6 address associated with a domain name, enabling access to websites over the newer IPv6 protocol.
• CAA records: Control which Certificate Authorities are authorized to issue certificates for a domain, enhancing security and preventing phishing attacks.
DNS Security
DNS security is paramount to protect websites and users from malicious attacks. Common security measures include:
• DNSSEC: Digitally signs DNS records to prevent spoofing and ensure data integrity.
• DDoS protection: Mitigates distributed denial-of-service attacks that attempt to overwhelm DNS servers and disrupt website access.
• DNS firewall: Filters and blocks malicious DNS queries to prevent unauthorized access and protect against data breaches.
DNS Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Regularly monitoring DNS performance and resolving issues promptly is crucial for maintaining website accessibility and performance:
• DNS monitoring tools: Allow real-time monitoring of DNS health, including uptime, resolution times, and security threats.
• DNS troubleshooting techniques: Involve using command-line tools, interpreting DNS error codes, and checking DNS propagation to identify and rectify issues.
New Trends in DNS Hosting
The DNS hosting landscape is constantly evolving with new technologies and trends emerging:
• DNS over HTTPS (DoH): Encrypts DNS queries to protect user privacy and prevent eavesdropping.
• DNS over TLS (DoT): Similar to DoH, DoT encrypts DNS queries but uses the TLS protocol instead of HTTPS.
• AI-powered DNS: Leverages artificial intelligence to optimize DNS performance, detect anomalies, and improve security.
DNS Load Balancing
DNS load balancing distributes incoming traffic across multiple servers, improving website performance and reliability. When users access a website, they are directed to the server with the lowest load, ensuring optimal response times and minimizing downtime.
Benefits of DNS load balancing include:
• Improved website performance: Reduces page loading times by distributing traffic evenly, ensuring a seamless user experience.
• Increased website reliability: If one server experiences an outage, the traffic is automatically redirected to other available servers, minimizing downtime and maintaining website accessibility.
DNS Failover
DNS failover ensures website availability by redirecting traffic to backup servers in the event of a primary server failure. When the primary server becomes unavailable, the DNS records are updated to point to the backup servers, providing seamless continuity.
Benefits of DNS failover include:
• Increased website uptime: Guarantees website accessibility even during server outages by providing a redundant backup solution.
• Minimized data loss: Prevents data loss by ensuring that website data and functionality are preserved across multiple servers.
DNS Analytics
DNS analytics provide valuable insights into DNS traffic patterns, website performance, and security threats. By analyzing DNS data, businesses can optimize their DNS settings, identify potential issues, and make informed decisions.
Benefits of DNS analytics include:
• Improved website performance: Identifies performance bottlenecks and allows for proactive measures to optimize DNS settings.
• Enhanced security: Detects suspicious DNS queries, anomalies, and potential security threats to protect against cyberattacks.
 Living Happy
Living Happy