In today’s fast-paced software development landscape, ensuring the quality of software applications has become increasingly crucial. With the advent of QA (Quality Assurance) automation, the process of testing and validating software has undergone a transformative shift.
Gone are the days of manual testing, fraught with human error and limited scalability. QA automation empowers testers to streamline their workflows, enhance accuracy, and accelerate the software development lifecycle. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of QA automation, exploring its benefits, challenges, and best practices.
Join us as we unlock the mysteries of this indispensable tool and empower you to harness its full potential.
Introduction to QA Automation
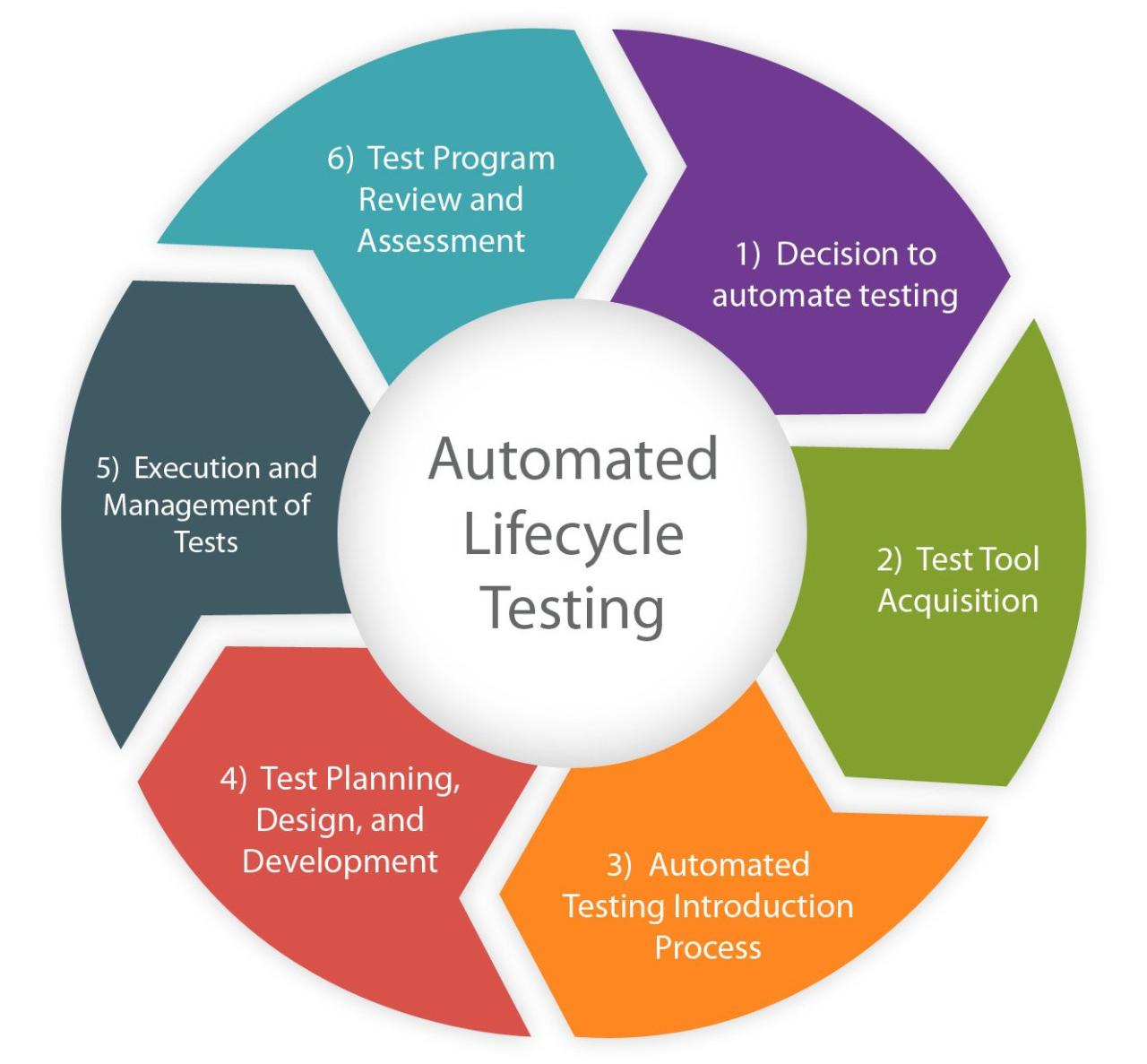
Welcome to the realm of QA automation, where technology and efficiency converge to revolutionize the software testing landscape. QA automation, often referred to as automated testing, is the process of using software tools to perform testing tasks that were traditionally carried out manually.
This automation streamlines the testing process, reduces human error, and enhances overall software quality.
For businesses, QA automation offers a multitude of benefits. It significantly reduces testing time and costs, enabling organizations to release high-quality software products faster. Additionally, automated testing improves accuracy and consistency, ensuring that software meets functional requirements and user expectations.
Types of QA Automation
The world of QA automation is vast, with various types of testing tools and techniques available. Each type serves a specific purpose and plays a crucial role in the overall testing process.
Unit Testing
Unit testing focuses on testing individual units or components of software code. It verifies that each unit functions as intended, ensuring that the building blocks of the software are reliable and robust. Unit testing tools like JUnit (Java) and NUnit (C) are commonly used for this purpose.
Integration Testing
Integration testing checks how different units or components of software work together. It ensures that the interfaces between these components are functioning as expected and that data is flowing correctly between them. Tools like Selenium and SoapUI are often employed for integration testing.
Functional Testing
Functional testing evaluates whether the software meets its specified requirements and performs as intended from the user’s perspective. Functional testing tools like Cucumber and Robot Framework help automate this process, ensuring that the software’s functionality aligns with user expectations.
Performance Testing
Performance testing assesses how the software behaves under different load conditions and usage patterns. It measures metrics such as response time, throughput, and resource utilization, ensuring that the software performs efficiently even under heavy usage. Performance testing tools like JMeter and LoadRunner are commonly used for this purpose.
Benefits of QA Automation
QA automation offers a plethora of benefits that enhance software development processes. These benefits range from reduced testing time and costs to improved accuracy and consistency. Let’s explore these advantages in greater detail.
One of the most notable benefits of QA automation is the significant reduction in testing time. Automated tests can execute test cases much faster than manual testers, enabling organizations to complete testing cycles in a fraction of the time. This accelerated testing process allows software teams to release new features and updates more frequently.
Moreover, QA automation significantly reduces testing costs. Automated tests can be executed repeatedly without the need for manual labor, reducing the dependency on expensive human resources. This cost savings can be substantial, especially for large-scale software projects with complex testing requirements.
QA automation also enhances the accuracy and consistency of software testing. Automated tests follow predefined test scripts, eliminating the potential for human error. Additionally, automated tests can be executed the same way every time, ensuring consistency in testing results and reducing the risk of false positives or negatives.
Challenges of QA Automation
While QA automation presents numerous benefits, it also comes with certain challenges that testers need to be aware of. These challenges include the need for skilled resources, the cost of automation tools, and the maintenance of automated test scripts.
One of the challenges of QA automation is the requirement for skilled resources. Implementing and maintaining automated tests requires testers with expertise in programming languages, testing methodologies, and automation tools. Finding and recruiting qualified QA automation engineers can be challenging, especially in competitive tech markets.
Another challenge is the cost of automation tools. Commercial QA automation tools can be expensive, especially for large-scale software projects. Organizations need to weigh the benefits and costs of automation tools carefully to determine the best approach for their specific needs.
Finally, automated test scripts require ongoing maintenance. As software evolves and new features are added, the corresponding test scripts need to be updated to ensure that they remain effective. This maintenance can be time-consuming and requires additional resources.
Best Practices for QA Automation
To maximize the benefits of QA automation and mitigate its challenges, it is crucial to adopt best practices that guide the implementation and maintenance of automated test scripts. These best practices include test case design, tool selection, and ongoing maintenance.
When designing test cases for automation, it is important to focus on the most critical and high-risk areas of the software. This approach ensures that the most valuable tests are automated, providing the greatest return on investment.
Selecting the right QA automation tool is also crucial. Organizations need to consider factors such as the software platform, test coverage requirements, and budget when choosing an automation tool. A well-suited tool will enhance testing efficiency and minimize the learning curve for testers.
Test Automation Framework
A test automation framework is a structure that provides the foundation for developing and executing automated tests. It defines the overall approach, test case organization, and common utilities used across the automation suite.
A well-designed framework streamlines the automation process, enhances code reusability, and facilitates test maintenance. Popular frameworks include Selenium WebDriver, Appium, and Robot Framework.
Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD)
Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD) are software development practices that aim to automate and streamline the build, test, and deployment processes.
CI involves integrating code changes into a shared repository frequently, triggering automated tests to verify the changes. CD extends CI by automating the deployment of approved code changes to production environments, reducing the risk of manual errors and enabling faster software releases.
Test Data Management
Test data management is crucial for ensuring the reliability and accuracy of automated tests. It involves creating and managing realistic test data that emulates real-world scenarios.
Proper test data management strategies prevent data conflicts, ensure data integrity, and enable the efficient execution of automated tests. It also helps maintain data privacy by anonymizing or masking sensitive information.
Test Environment Management
Test environment management involves setting up and managing the necessary infrastructure and resources for executing automated tests.
This includes creating test environments, provisioning test servers, and configuring network and security settings. Effective test environment management ensures the availability, stability, and consistency of the testing environment, reducing test failures caused by environmental issues.
Reporting and Analytics
Reporting and analytics are essential for monitoring the performance and effectiveness of QA automation. Automated testing tools generate test reports that provide insights into test results, execution times, and defect metrics.
Analyzing these reports helps teams identify areas for improvement, optimize test suites, and demonstrate the value of QA automation to stakeholders. Visualization tools can further enhance reporting by presenting test results in user-friendly dashboards and graphs.
 Living Happy
Living Happy