In the realm of academia, the quest for knowledge often comes with a hefty price tag. ‘Student finance’, a term encompassing the various funding options available to aspiring scholars, plays a pivotal role in unlocking the gateway to higher education.
Whether it’s scholarships, grants, loans, or a combination thereof, understanding the nuances of student finance is paramount for navigating the complexities of modern education. This article aims to demystify the world of student finance, providing comprehensive insights into the different types of funding, eligibility criteria, and strategies for managing educational expenses.
By shedding light on these crucial matters, we empower students to make informed decisions, overcome financial hurdles, and embark on their academic journeys with confidence and clarity.
Student Finance: Understanding the Basics
Navigating the world of higher education can be daunting, especially when it comes to financing your studies. Student finance is an essential aspect of planning for college, and understanding the various options available can help you make informed decisions about your financial future.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the ins and outs of student finance, providing clear and concise information to empower you in your journey towards higher education.
Types of Student Finance
There are several types of student finance available, each with its unique characteristics and eligibility criteria. Here’s a breakdown of the most common options:
- Grants: Free money that does not need to be repaid. Typically based on financial need and academic merit.
- Scholarships: Similar to grants, but often awarded based on specific criteria, such as academic achievement, athletic ability, or community involvement.
- Loans: Money that must be repaid with interest.
Federal and private loans are available, with different interest rates and repayment terms.
- Work-Study Programs: Part-time jobs on or off campus that allow students to earn money while they study.
Applying for Student Finance
The process of applying for student finance can vary depending on the type of aid you’re seeking. Here are the general steps involved:
- Complete the FAFSA (Free Application for Federal Student Aid): This is the main application used to determine your eligibility for federal and state financial aid.
- Research scholarships and grants: Explore various scholarship and grant databases to identify opportunities that fit your qualifications.
- Apply for loans as needed: If you need additional funding, consider applying for federal or private student loans.
- Submit all required documentation: Make sure to provide all necessary documents, such as transcripts and proof of income, to support your application.
- Create a budget: Track your income and expenses to ensure you’re living within your means.
- Avoid unnecessary expenses: Prioritize essential items and cut back on non-essential expenses.
- Explore loan consolidation and repayment options: If you have multiple student loans, consider consolidating them to simplify repayment.
- Make timely payments: Staying current on your loan payments can help you build a positive credit history and avoid penalties.
- Federal Student Aid Information Center: Provides comprehensive information and support on all aspects of federal student aid. (1-800-433-3243)
- CollegeBoard: Offers a wealth of information on college admissions, financial aid, and scholarships.
- Sallie Mae: A private student lender that provides resources and tools for student finance.
Managing Your Student Finance
Once you receive student finance, it’s crucial to manage it wisely. Here are some tips for responsible spending and repayment:
Additional Resources for Student Finance
For further assistance with student finance, here are some valuable resources:
Eligibility Criteria for Student Finance
Grants
To qualify for grants, students must demonstrate financial need. This is determined by their family’s income and assets. Some grants also have academic merit requirements, such as maintaining a certain GPA.
Federal grants include the Pell Grant, which is available to low-income students, and the Supplemental Educational Opportunity Grant (SEOG), which is awarded to students with exceptional financial need.
Scholarships
Scholarships are awarded based on various criteria, including academic achievement, athletic ability, artistic talent, and community involvement. Some scholarships are also available to students from specific backgrounds or who are pursuing certain fields of study.
There are many different types of scholarships available, including those offered by universities, private organizations, and corporations. Students should research scholarship opportunities carefully to identify those that fit their qualifications.
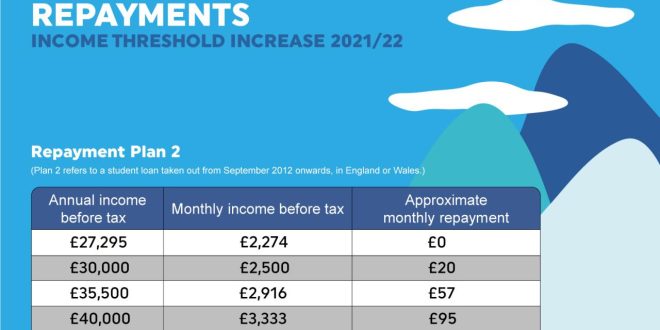
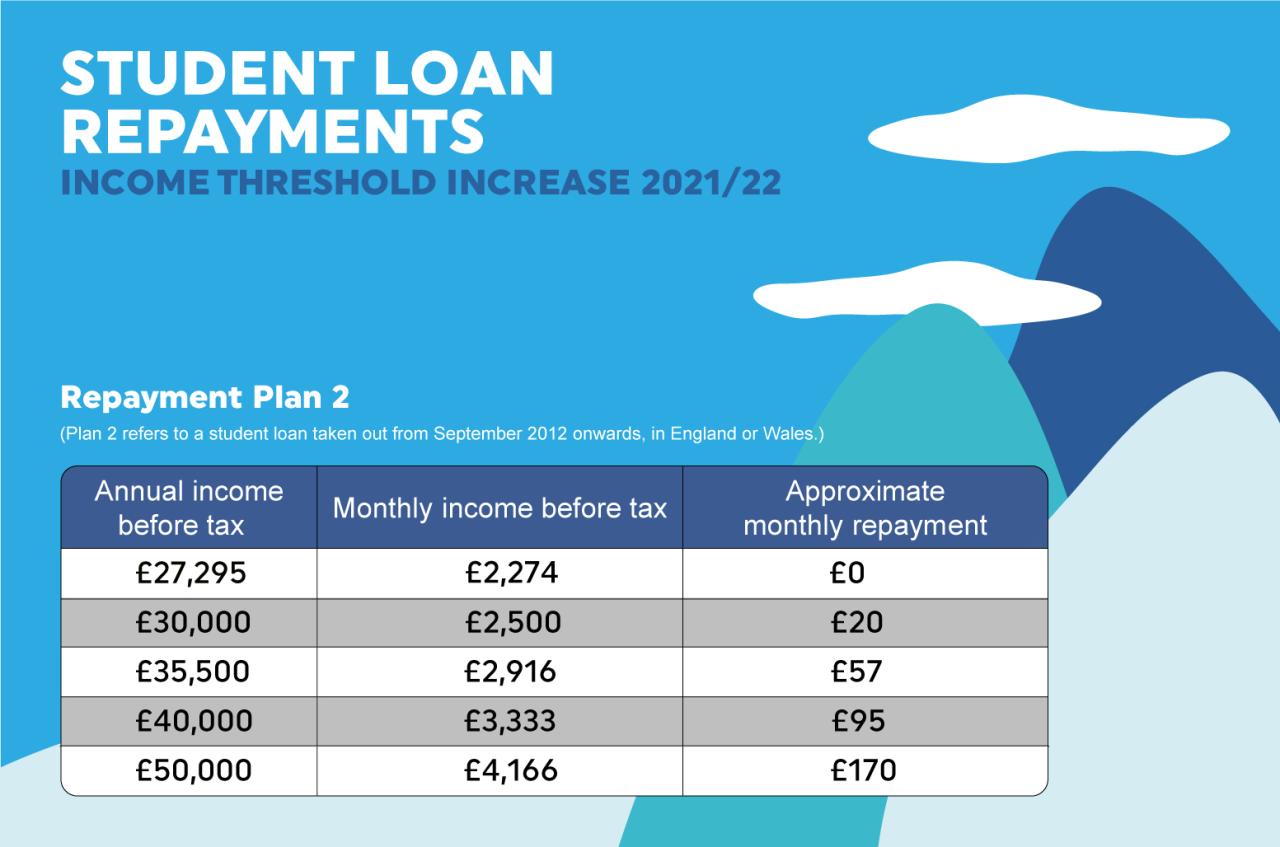
Repayment Strategies for Student Loans
Federal Student Loans
Federal student loans offer a variety of repayment plans, including standard repayment, extended repayment, and income-driven repayment plans. Standard repayment typically takes 10 years, while extended repayment can take up to 25 years.
Income-driven repayment plans tie your monthly payments to your income, making them more affordable if you have a low income. These plans can extend the repayment period to 20 or 25 years, but they can also provide loan forgiveness if you make payments on time for the full term.
Private Student Loans
Private student loans typically have higher interest rates and less flexible repayment options than federal student loans. Some private lenders offer extended repayment plans or loan consolidation options, but these may come with additional fees or penalties.
It’s important to compare interest rates and repayment options carefully before choosing a private student loan. You should also consider the possibility of loan consolidation in the future, which can help you lower your monthly payments and simplify repayment.
The Impact of Student Debt
Long-Term Financial Consequences
Student debt can have a significant impact on your long-term financial health. High student loan payments can make it difficult to save for other financial goals, such as buying a house or retiring. Student debt can also affect your credit score, which can impact your ability to qualify for other loans or credit cards.
If you have a lot of student debt, it’s important to develop a plan to manage it effectively. This may involve making extra loan payments, consolidating your debt, or refinancing your loans for a lower interest rate.
Social and Economic Implications
Student debt has also been linked to a number of social and economic issues, including income inequality and racial disparities. Borrowers with high student debt are more likely to experience financial stress, unemployment, and housing instability.
The rising cost of higher education has made student debt a major financial burden for many Americans. It’s important to address the systemic issues that contribute to student debt and to provide students with affordable options for financing their education.
 Living Happy
Living Happy