Within the depths of every umbilical cord lies a treasure trove of life-saving potential—cord blood. Rich in stem cells that hold the power to treat a vast array of illnesses, cord blood donation has emerged as a beacon of hope in the fight against life-threatening conditions.
Join us as we delve into the world of cord blood donation, uncovering its profound significance and unraveling the challenges that shape its path. From its therapeutic capabilities to the logistics of collection and storage, this article will illuminate the intricacies of this vital practice, empowering you with knowledge that can make a tangible difference in the lives of countless patients.
Cord Blood Donation: A Comprehensive Guide
What is Cord Blood Donation?
Cord blood is the blood that remains in the umbilical cord and placenta after a baby is born. It contains stem cells that can be used to treat a variety of diseases.
Cord blood donation involves collecting and storing these stem cells for future use.
Cord blood stem cells are different from embryonic stem cells, which are obtained from embryos fertilized for research purposes. Cord blood stem cells are collected after the baby is born and do not harm the mother or child.
Why is Cord Blood Donation Important?
Cord blood donation is important because it provides a valuable source of stem cells that can be used to treat a variety of diseases. These diseases include leukemia, lymphoma, sickle cell disease, and other blood disorders.
Cord blood donation is also important because it is a safe and painless procedure.
The collection of cord blood does not harm the mother or baby, and it only takes a few minutes. Cord blood can be collected from any healthy pregnant woman who is over 18 years old.
How to Donate Cord Blood
If you are interested in donating cord blood, you should first talk to your doctor. Your doctor can provide you with more information about the donation process and help you decide if it is right for you.
Once you have decided to donate cord blood, you will need to contact a cord blood bank.
The cord blood bank will provide you with a collection kit and instructions on how to collect and store the cord blood.
Benefits of Cord Blood Donation
There are many benefits to donating cord blood. – First, you will be providing a valuable gift to someone in need. – Second, you will be helping to advance medical research.
– Third, you will be giving your child the option of using their own stem cells for medical treatment in the future.
Risks of Cord Blood Donation
There are few risks associated with cord blood donation. The most common risk is that the cord blood will not be viable for storage. This is because cord blood must be collected within a certain amount of time after the baby is born.
Other risks of cord blood donation include:
– Bruising or swelling at the collection site
– Infection at the collection site
– Allergic reaction to the collection materials
Cord Blood Collection and Storage
Collection Process
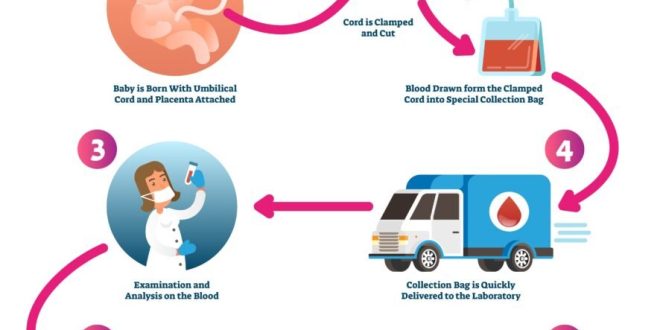
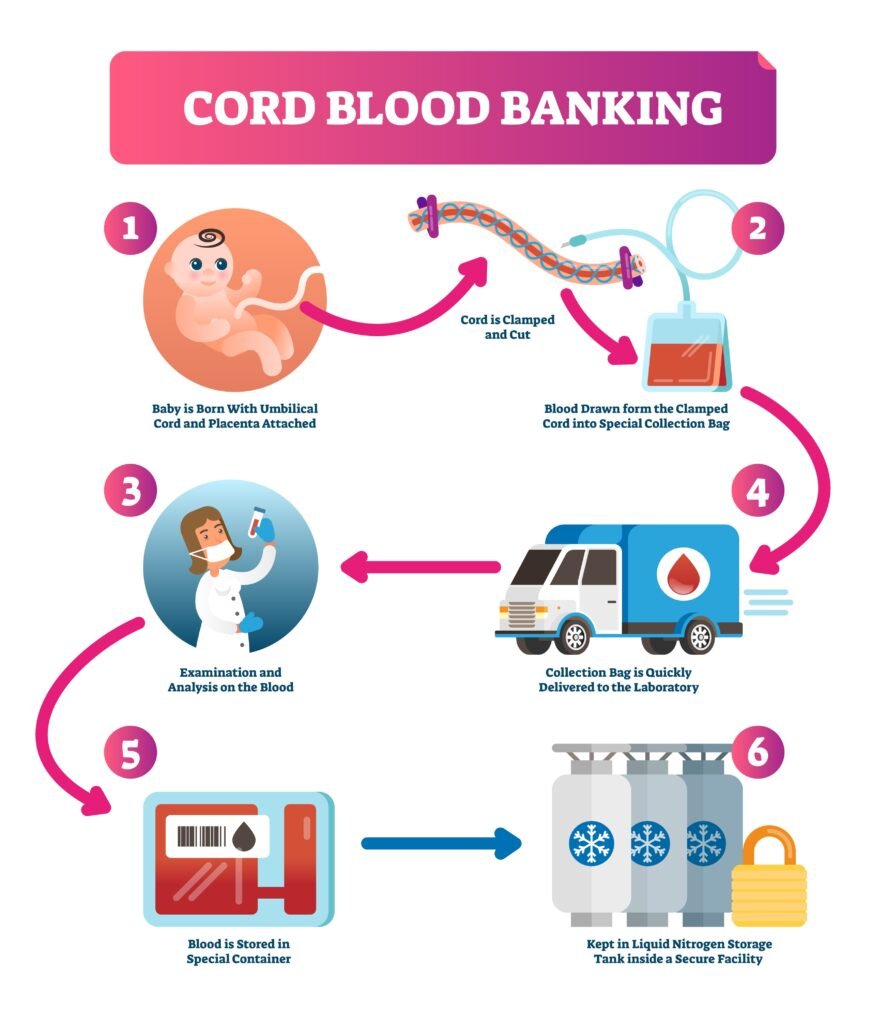
Cord blood collection is a relatively simple procedure that typically takes only a few minutes. It is usually performed immediately after the baby is born, once the umbilical cord has been clamped and cut.
The blood is collected from the umbilical vein using a sterile needle and syringe. The collected blood is then placed in a special collection bag that prevents contamination and preserves the stem cells.
Storage Options
Once the cord blood has been collected, it is stored in a cryogenic storage facility. These facilities use liquid nitrogen to maintain the blood at extremely low temperatures, preserving the stem cells for long-term use.
Cord blood can be stored for many years in cryogenic storage, allowing it to be used for future medical treatments if needed.
Therapeutic Applications of Cord Blood
Blood Disorders
Cord blood stem cells have been successfully used to treat a variety of blood disorders, including leukemia, lymphoma, and sickle cell disease. These disorders are characterized by abnormal or insufficient production of blood cells, which can lead to life-threatening complications.
Cord blood stem cell transplantation can provide a healthy source of blood-forming stem cells, helping to restore normal blood cell production and improve the patient’s overall health.
Immunological Disorders
Cord blood stem cells have also shown promise in treating immunological disorders, such as severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) and certain autoimmune diseases. In these conditions, the immune system is either underdeveloped or overactive, leading to vulnerability to infections or damage to healthy tissues.
Cord blood stem cell transplantation can help restore a healthy immune system, improving the patient’s ability to fight infections and regulate immune responses.
Challenges and Opportunities in Cord Blood Donation
Matching Challenges
One challenge associated with cord blood donation is finding a compatible recipient for the stem cells. Unlike bone marrow transplants, which require a high degree of genetic matching between donor and recipient, cord blood transplants have a higher tolerance for genetic variations.
However, finding a fully compatible cord blood unit can still be challenging, especially for patients from certain ethnic backgrounds.
Cord Blood Banking
Public vs. Private Banking
Cord blood can be banked either publicly or privately. Public cord blood banks store cord blood units that are available for anyone in need. Private cord blood banks store cord blood units for the exclusive use of the donor’s family.
The choice between public and private banking depends on several factors, including the donor’s financial situation, family history of diseases, and the availability of compatible public cord blood units.
Cost and Availability
Private cord blood banking typically costs several thousand dollars for collection and storage. Public cord blood banking is generally free or low-cost, but the availability of compatible units may be limited.
Families considering private banking should carefully weigh the benefits and costs, as well as the likelihood of needing to use their stored cord blood.
Ethical Considerations in Cord Blood Donation
Informed Consent and Autonomy
Informed consent is essential in cord blood donation. Pregnant women should be fully informed about the potential benefits and risks of donation, as well as the implications for their child’s future health.
Respect for patient autonomy is paramount, and individuals should be given the freedom to make decisions about their own bodies and the use of their child’s cord blood.
Equity and Access
Equitable access to cord blood donation and transplantation services is a critical concern. Socioeconomic factors and ethnic disparities can impact the availability and accessibility of cord blood banking for certain populations.
Addressing these inequities is essential to ensuring that all individuals have the opportunity to benefit from this life-saving treatment.
Global Initiatives and Research
International Cord Blood Banks
Cord blood banks have been established in countries around the world, creating a global network for stem cell donation and transplantation.
Collaboration and data sharing among international banks enhance the chances of finding compatible matches for patients in need.
Ongoing Research and Advancements
Research in the field of cord blood donation and transplantation is ongoing, with scientists exploring novel applications and improving transplantation outcomes.
Areas of research include improving cord blood viability, reducing graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), and expanding the therapeutic potential of cord blood stem cells.
 Living Happy
Living Happy