Dementia is not a single disease, but rather a group of symptoms affecting cognitive abilities, such as memory, thinking, and reasoning. These symptoms are severe enough to interfere with daily life. It’s important to understand the various causes, symptoms, and management strategies associated with dementia to provide appropriate care and support for affected individuals and their families. This article will explore these key aspects in detail, and hopefully, give you a clearer picture of what it’s all about. Honestly, it’s something we all need to be more aware of, isn’t it?
Defining Dementia
Dementia is really an umbrella term, you know? It describes a decline in mental ability that’s severe enough to mess with your day-to-day life. It’s not one specific disease, but rather a bunch of symptoms caused by different underlying brain disorders. Think of it like this: it’s the overall effect, not the single cause.
Dementia vs. Alzheimer’s Disease
Okay, this is where it gets a little tricky. People often use “dementia” and “Alzheimer’s” like they’re the same thing. But they’re not! Alzheimer’s disease is actually the most common cause of dementia, accounting for something like 60-80% of all cases. So, Alzheimer’s is a type of dementia, but not all dementia is Alzheimer’s. Got it? I hope so!
Types of Dementia
Alzheimer’s Disease
So, Alzheimer’s, as we just mentioned, is the big one. It’s characterized by these weird buildups of amyloid plaques and tau tangles in the brain. Sounds like something out of a sci-fi movie, right? Anyway, these things lead to progressive memory loss and cognitive decline. It’s a tough one, no doubt.
Vascular Dementia
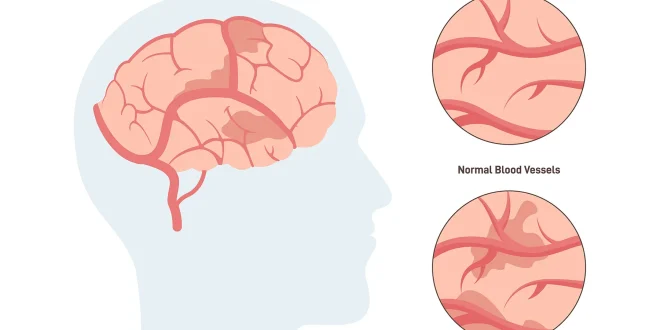
Now, this is a different beast altogether. Vascular dementia is caused by reduced blood flow to the brain. Think stroke, or other vascular problems. The symptoms can vary a lot, depending on what area of the brain is affected. It’s a bit like a damaged pipe in your house – where it leaks determines the problem, you know?
Lewy Body Dementia
Lewy Body Dementia involves these abnormal deposits of alpha-synuclein protein – they call ’em Lewy bodies – in the brain. These cause a whole cocktail of issues: cognitive decline, visual hallucinations (yikes!), and even movement problems. Honestly, it sounds incredibly unsettling.
Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD)
FTD affects the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain – hence the name! This one leads to changes in personality, behavior, and language. It can be particularly hard on families, as it can really change who a person is at their core.
Symptoms of Dementia
Cognitive Symptoms
Let’s talk symptoms. On the cognitive side, we’re talking memory loss, difficulty with reasoning and problem-solving, confusion, disorientation, and trouble with language. Basically, the things that make it hard to navigate daily life. Ever had that “where did I put my keys?” moment? Imagine that, but all the time… and with bigger things.
Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms
Dementia isn’t just about memory, though. It can also cause some pretty significant behavioral and psychological changes. We’re talking personality shifts, mood swings, agitation, anxiety, depression, and, in some cases, even hallucinations and delusions. It’s a lot, I know.
Physical Symptoms
And, depending on the type of dementia, there can be physical symptoms too. Things like movement problems, tremors, stiffness, and difficulty with coordination. It really underscores how dementia is a disease that affects the whole person.
Diagnosis of Dementia
Medical History and Physical Exam
So, how do doctors figure out if someone has dementia? Well, it starts with a thorough medical history, including family history (that’s important!). Then, a physical exam to assess overall health and rule out other possible causes. It’s all about piecing the puzzle together.
Cognitive and Neurological Tests
Next up are cognitive tests, which assess things like memory, attention, language, and problem-solving skills. Then, neurological tests evaluate reflexes, balance, and motor function. These tests help get a clearer picture of how the brain is working, or not working, as the case may be.
Brain Imaging
Finally, brain imaging – MRI, CT, and PET scans – can help identify brain abnormalities. Things like atrophy (shrinkage), lesions, or those abnormal protein deposits we talked about earlier. It’s like taking a look under the hood to see what’s going on.
Treatment and Management of Dementia
Medications
Okay, so what can be done about it? Sadly, there’s no cure for most types of dementia. But medications can help manage symptoms and slow down the progression of the disease in some cases. Things like cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine. It’s not a fix, but it can make a difference.
Therapies
Then there are the therapies: occupational therapy, speech therapy, and physical therapy. These can help individuals with dementia maintain their independence and improve their quality of life. It’s all about finding ways to adapt and keep living as fully as possible.
Lifestyle Modifications
And don’t underestimate the power of lifestyle! Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and mental stimulation can all help support brain health and slow down cognitive decline. It’s about keeping the brain active and engaged.
Support for Caregivers
Here’s a really important point: caring for someone with dementia is tough. It’s emotionally and physically draining. Support groups, respite care, and counseling can provide caregivers with the resources they need to cope. It’s crucial that they don’t feel alone.
Prevention of Dementia
Risk Factors
Can we prevent dementia? Well, some risk factors, like age and genetics, are out of our control. But others, like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, obesity, and smoking, can be managed through lifestyle changes. So, there’s definitely something we can do to reduce our risk.
Healthy Lifestyle
Bottom line: adopting a healthy lifestyle – regular exercise, a healthy diet, mental stimulation – can really help reduce the risk of developing dementia. It’s about investing in your brain health now, for the future. Kind of like saving for retirement, but for your mind!
Ongoing Research
The good news is that research is ongoing, constantly seeking new treatments and prevention strategies. Clinical trials are super important for advancing our understanding of dementia. So, there’s hope on the horizon!
Hopefully, this has given you a better understanding of dementia – what it is, the different types, the symptoms, and what can be done about it. It’s a complex and challenging issue, but with knowledge and understanding, we can better support those affected and work towards a future with better treatments and prevention strategies. Take care of your brain, folks, and don’t forget to share this information with others. Who knows, it might make a real difference in someone’s life.
 Living Happy
Living Happy