In the intricate tapestry of a nation’s progress, education policy weaves threads vital to its future. It guides the decisions that shape our children’s minds, prepares them for the challenges of a rapidly evolving world, and ultimately determines the contours of our collective societal well-being.
Education policy encompasses the frameworks, regulations, and funding mechanisms that govern educational systems, ensuring access to quality learning opportunities for all. As we navigate the complexities of modern education, it is imperative to explore the challenges, trends, and best practices that inform these policies, empowering us to forge a path towards equitable and transformative learning experiences.
Education Policy: A Comprehensive Guide
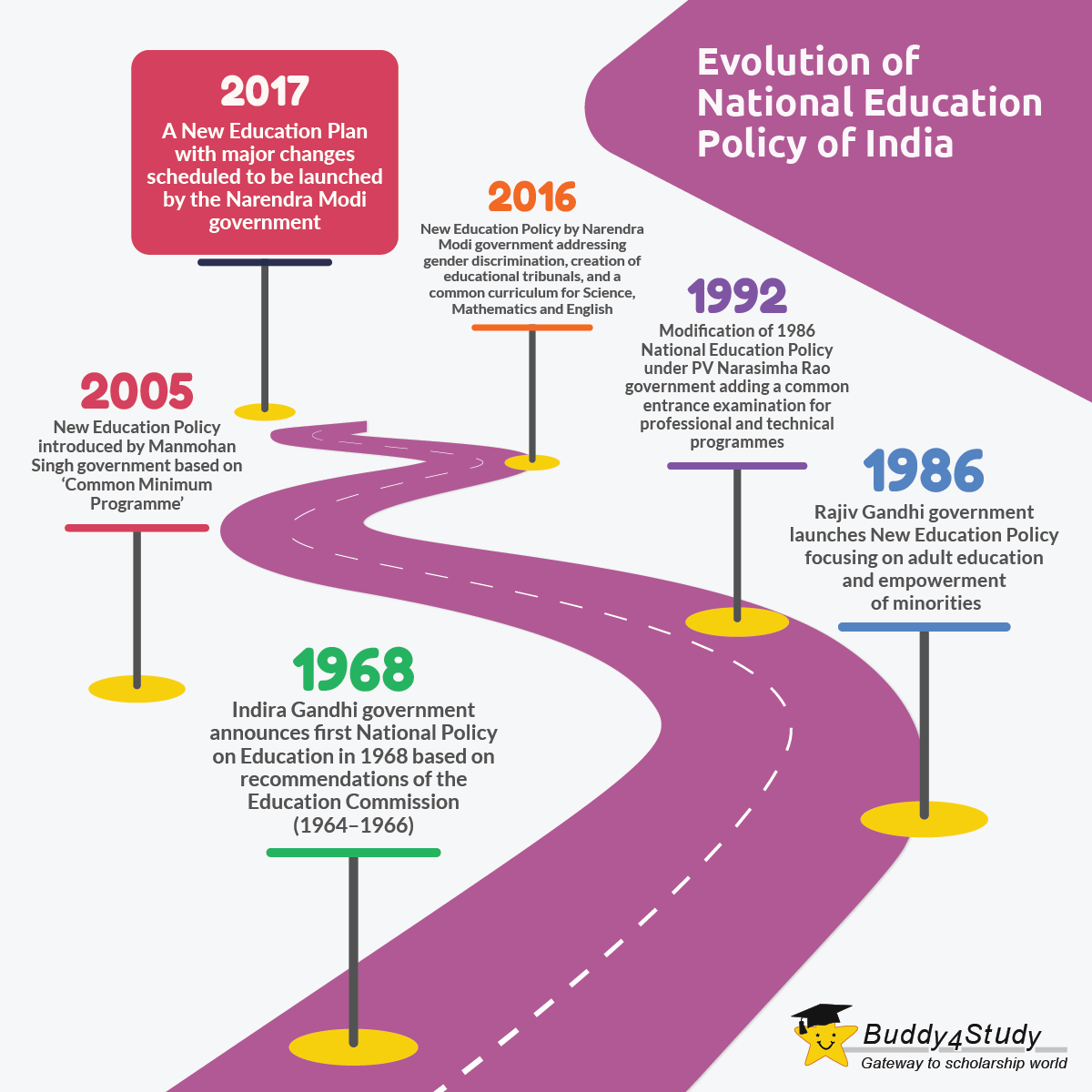
Education policy encompasses the laws, regulations, and guidelines that govern the education system within a specific jurisdiction. It plays a pivotal role in shaping the structure, curriculum, funding, and overall quality of education provided to students.
Education policy is typically developed and implemented by governments or educational authorities.
The primary objective of education policy is to ensure that all students have access to equitable and high-quality education that enables them to reach their full potential. It involves setting educational standards, allocating resources, and addressing specific issues or challenges within the education system.
Education policy encompasses a wide range of areas, including curriculum development, teacher training, student assessment, funding allocation, and governance structures. It is constantly evolving and adapting to meet the changing needs of society and the demands of a globalized economy.
Developing and implementing effective education policies requires a collaborative effort involving policymakers, educators, parents, and community stakeholders. It is essential to consider research, best practices, and evidence-based approaches to ensure that policies are grounded in sound principles and achieve their intended outcomes.
Key Components of Education Policy
The key components of education policy include:
- Curriculum and Standards: Defining the knowledge, skills, and values that students are expected to acquire at each level of education.
- Assessment and Evaluation: Establishing procedures for assessing student learning and evaluating the effectiveness of educational programs.
- Teacher Training and Professional Development: Providing opportunities for teachers to enhance their skills and knowledge to meet the evolving needs of students.
- Funding and Resource Allocation: Ensuring adequate financial resources are available to support educational programs and initiatives.
- Governance and Administration: Establishing structures for managing and overseeing the education system, including school boards, educational authorities, and government agencies.
Challenges and Emerging Trends
Education policy is constantly facing challenges and evolving in response to emerging trends. Some of the key challenges and trends include:
- Equity and Access: Ensuring all students have equal opportunities to high-quality education, regardless of their background or circumstances.
- Technology and Innovation: Integrating technology into education to enhance learning experiences and prepare students for the digital age.
- Globalization and Internationalization: Addressing the impact of globalization on education and preparing students for a globalized economy.
- Sustainability and Environmental Education: Incorporating environmental principles into education to promote sustainability and responsible citizenship.
Education Policy and Social Justice
Education policy has profound implications for social justice, as it can promote or hinder the achievement of equitable outcomes for all students. An education policy that promotes social justice aims to address systemic barriers and inequities that prevent certain groups of students from accessing and succeeding in education.
Key principles of a socially just education policy include:
- Equity of Access: Ensuring that all students have equal opportunities to enroll in and complete high-quality educational programs.
- Cultural Responsiveness: Recognizing and valuing the diverse backgrounds and experiences of students, and incorporating them into the curriculum and teaching practices.
- Anti-Discrimination: Prohibiting discrimination based on race, gender, ethnicity, religion, sexual orientation, or disability.
- Resource Allocation: Providing additional resources and support to schools and students who face specific challenges or disadvantages.
- Community Engagement: Engaging with parents, community organizations, and other stakeholders to ensure that education policies reflect the needs and values of the community.
International Perspectives on Education Policy
Education policy varies significantly across countries, reflecting different cultural values, economic priorities, and political ideologies. Studying international perspectives on education policy can provide valuable insights and lessons for improving education systems.
Key areas of comparison include:
- Curriculum and Standards: Examining the content and structure of curricula in different countries.
- Assessment and Evaluation: Comparing approaches to student assessment and the use of standardized testing.
- Teacher Training and Professional Development: Evaluating the quality and effectiveness of teacher training programs.
- Governance and Administration: Understanding the structures and processes for managing and overseeing education systems.
- Funding and Resource Allocation: Analyzing how countries allocate resources for education and the impact on student outcomes.
Education Policy and the Future of Work
Education policy has a crucial role to play in preparing students for the rapidly changing world of work. The increasing automation of tasks and the emergence of new technologies require education systems to adapt and equip students with the skills and knowledge they need to succeed in the future workforce.
Key areas of focus include:
- STEM Education: Emphasizing science, technology, engineering, and mathematics education to develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and innovation skills.
- Skills Development: Providing opportunities for students to acquire technical and vocational skills, such as coding, data analytics, and robotics.
- Career Exploration: Exposing students to different career paths and providing them with guidance and support to make informed choices.
- Lifelong Learning: Encouraging students to continue learning and adapting throughout their lives to keep pace with technological advancements and changing workforce demands.
Education Policy and the Environment
Education policy can also play a significant role in promoting environmental sustainability and responsible citizenship. By incorporating environmental principles into curricula and teaching practices, education systems can help students develop an understanding of environmental issues and the importance of conservation.
Key areas of focus include:
- Environmental Education: Integrating environmental science, ecology, and sustainability concepts into all levels of education.
- Outdoor Learning: Providing opportunities for students to connect with nature and learn about the environment through hands-on experiences.
- Sustainable Practices: Promoting sustainable practices in schools, such as recycling, composting, and reducing energy consumption.
- Climate Change Education: Raising awareness about the causes and impacts of climate change and empowering students to take action.
 Living Happy
Living Happy